Computing Bias - Hanlun
What is it?
- Computing bias is a bias that exists within algorithms that unfairly discriminate against certain individuals or groups, creating unfair outcomes
- Computing innovations reflect biases because algorithms and data are influenced by the people who contributed to it, so computing biases can be embedded at every level of development
- Algorithm bias should be reduced so computer innovations can combat existing user bias

Popcorn Hack #1:
Which of the following scenarios is an example of computing bias?
A. An email filtering system accurately categorizes emails into spam and non-spam based on a diverse set of features, minimizing false positives and false negatives.
B. A navigation app provides real-time traffic updates and alternate routes to users, considering various factors such as traffic volume, road closures, and weather conditions.
C. An image recognition algorithm identifies objects in photographs with high accuracy, regardless of the gender, ethnicity, or age of the individuals depicted.
D. An automated hiring system consistently favors candidates from specific educational institutions and backgrounds, resulting in the exclusion of qualified applicants from diverse backgrounds.
D is the right answer!
Types of Computing Bias - Trevor
Computing bias can be either intentional or unintentional and as said before, this bias is a result of human biases in development. Here are some examples:
- Data bias: when the data set does not reflect the real world values
- Ex: A company is developing an algorithm to see whether or not a product has positive or negative online reviews. However, the training data might over-represent overly negative or positive opinions that are posted online which wouldn’t reflect the real-world popularity of the product
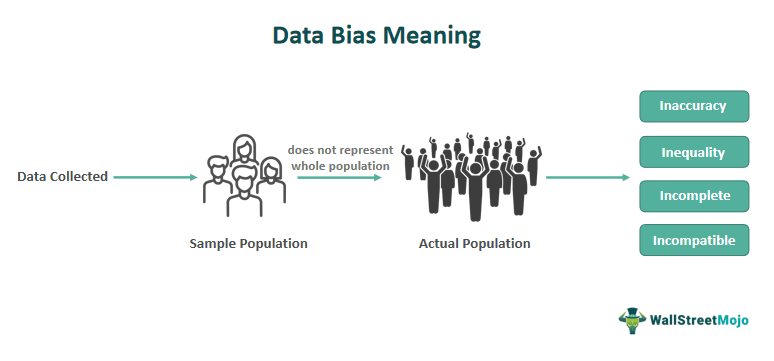
- Ex: A company is developing an algorithm to see whether or not a product has positive or negative online reviews. However, the training data might over-represent overly negative or positive opinions that are posted online which wouldn’t reflect the real-world popularity of the product
- Human bias: People who make the programs may bring in their own biases whether consciously or unconsciously
- Ex: A software development team is working on a code review algorithm. They all have experience using Language X and so they believe that developers using Language X are more qualified and so their algorithm reflects that. This uses their individual traits and applies it to the entire group of coders using Language X.
- Algorithmic bias reflects the data bias and human bias and often amplifies it. However, bias can arise from the structure and decision making of the program itself
- Ex: A program is designed to automate the loan approval system. It uses information from income, employment history, and credit score. However, the algorithmn can produce biased results based on trends from certain job occupations which may disproportionally affect certain groups
There are many more nuanced types of computing biases which you can find here: https://developers.google.com/machine-learning/crash-course/fairness/types-of-bias
- Ex: A program is designed to automate the loan approval system. It uses information from income, employment history, and credit score. However, the algorithmn can produce biased results based on trends from certain job occupations which may disproportionally affect certain groups
Popcorn Hack #2:
An online example of computing bias is when an HP computer’s facial recognition system couldn’t track the face of someone with darker skin. Why is this and what type of bias is it? Do you think it was intentional or unintentional?
It is data bias!
Explicit and Implicit Data - Lakshanya
- Explicit data is information you give an app or site
- Implicit data is the information it collects based on your activity
- For example, with Netflix, the explicit data it collects includes your rating of movies (thumbs up, thumbs down) and your personal information. The implicit data it collects includes when you watch, what you binge, and the frequently selected genres.
- This data collection is also known as user bias. More bias comes in when Netflix shows its exclusives before any of the regular items to gain subscriptions.
Popcorn Hack #3:
- What is another scenario of data collection in everyday applications and situations?
Tiktok algorithms, cookies, GPS tracking ur location, etc
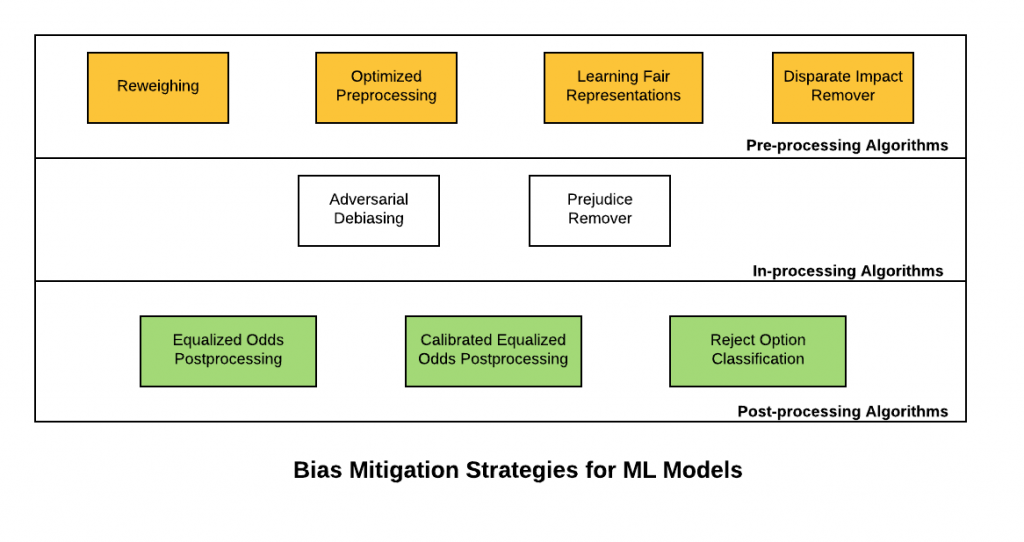
Mitigation Strategies: - Matthew
- Obtain more diverse data (ex: racist computer)
-
Pre-processing: Writing an algorithm that adjusts to datasets to check for bias before using it as an input. It’s about cleaning up and organizing the raw data and makes it more suitable for building or training models.
- In-processing: This occurs during the processing or analysis of data within a system or model. The algorithm will manipulate and transform the data as it goes through the model during its active use.(ex: if the algorithm was processing images it would rescale the image to keep consistent dimensions)
More Mitigation Strategies: - Aditya
Post-processing: This type of strategy is comprised of 3 parts, input correction, classifier correction, output correction
Input Correction:
What it is: Imagine you have a machine learning model that identifies objects in images. Input correction involves making adjustments to the images used to test the model after it has already been trained.
Example: If the model was trained mostly on pictures taken during the day, input correction might involve adjusting the brightness and color balance of images taken at night to make them more comparable.
Classifier Correction:
What it is: This step focuses on fine-tuning the algorithm or model after training to reduce any biases or discrimination it might have inadvertently learned.
Example: Suppose you have a model for hiring decisions, and you notice it tends to favor certain demographics. Classifier correction could involve tweaking the decision-making rules to ensure fair treatment for all groups.
Output Correction:
What it is: After the model makes predictions, output correction involves modifying those predictions to eliminate any biases or unwanted discrimination.
Example: If a language translation model tends to produce more errors when translating sentences from one language to another, output correction might involve adjusting the final translated sentences to be more accurate and fair.
In summary, post-processing is like a three-step check and adjustment process to ensure that a machine learning model behaves fairly and accurately, even after it has been trained. Input correction modifies the testing data, classifier correction fine-tunes the model, and output correction adjusts the final predictions. This helps in addressing issues like biases and discrimination that may arise during the model training process.
Homework:
Problem: Biased Predictive Policing Algorithm: A city implements a predictive policing algorithm to allocate law enforcement resources more efficiently. However, concerns arise as community members and activists notice that the algorithm appears to disproportionately target certain neighborhoods, leading to over-policing and potential violations of civil rights. Provide a solution to how this situation can be resolved, and how the computing bias can be removed. Explain which method of mitigation you will use and how it works.
We can use Classifier Correction. By focusing on Classifier Correction, the goal is to modify the decision-making process of the algorithm itself. This method aims to eliminate biases and ensure that law enforcement resources are allocated fairly and without discrimination across different neighborhoods. Through this, the the computing bias can be removed and this situation can be resolved. Therefore, biases/discrimination would be eliminated to ensure fair treatment for all groups (similar to the example shown above)
Reflective Summary: Computing Bias Lesson on Nighthawk-Pages
Title: Computing Bias Lesson
Published: December 11, 2023
Reading Time: Approx. 6 minutes
I’m writing to share my reflections on the Computing Bias Lesson available on Nighthawk-Pages. The lesson was an interesting exploration into the intricate realm of computing biases. Through this experience, I gained valuable insights:
Understanding Bias Types:
The lesson delved deep into the various biases prevalent in algorithms, emphasizing both intentional and unintentional biases. I gained an understanding of data bias, human bias, and algorithmic bias and how these biases intersect to impact technological innovations.
Real-world Scenarios:
The practical examples, such as the HP facial recognition system encountering data bias and the implications of biased predictive policing algorithms, elucidated how biases manifest in everyday technology.
Mitigation Strategies:
Exploring diverse mitigation strategies was interesting. Concepts like pre-processing, in-processing, and post-processing methods to identify and rectify biases embedded in algorithms.
Problem-solving Approach:
The homework scenario involving mitigating biased predictive policing algorithms by implementing Classifier Correction showcased practical problem-solving skills to address real-world biases in technology.
Reflective Insights:
This lesson has broadened my perspective on the pervasive issue of biases in computing. It has equipped me with a foundational understanding of identifying, addressing, and mitigating biases in technology.
